pH >12 • Radiopaque • Non-Setting
Description:
All Purpose, Non-Setting Calcium Hydroxide Paste
For Vital Pulp Therapy and Root Canal Therapy
Multi-Cal is a smooth, creamy calcium hydroxide preparation recommended for all clinical applications where calcium hydroxide is indicated.
Temporary and Intermediate Root Canal Therapy
- For routine use as an intracanal dressing between office visits
- Non-surgical solution for abscessed teeth and failed root canals
- For treatment of abscesses, cysts, periapical lesions, root resorption, root fractures, perforations, apexification, pus, hemorrhage, exudation, weeping canals
- Treatment of traumatic injuries
- Non-setting. Easily removed with file and irrigation.
Vital Pulp Therapy
- Direct Pulp Capping, Pulpal Curettage, Pulpotomy
- Dentin Bridge Formation
- Cavity Lining and Indirect Pulp Capping
Code and Description:
MULTI – Multi-Cal Kit: 4 x 1.2 mL syringes + 8 applicator tips
MULTI-3 – Multi-Cal: 3 mL syringe

22D20 – Dark Blue, 22 ga x 1/2″, Prebent Tips, Pkg. 20 Use with Multi-Cal & Dentin Conditioning Gel

22D100 – Dark Blue, 22 ga x 1/2″, Prebent Tips, Pkg. 100 Use with Multi-Cal & Dentin Conditioning Gel
Applicator Tip:
Related products
Clinical Procedure
Root Canal Therapy
Pulpdent Paste, TempCanal and Multi-Cal are used in endocontics for all the following clinical situations outlined by Dr. G.S. Heithersay:
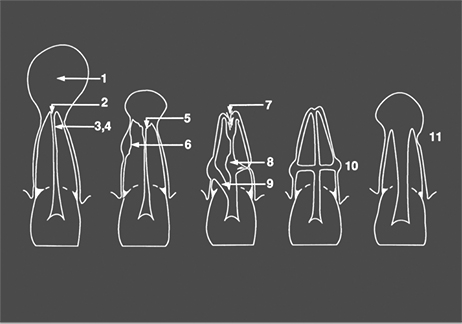
1. Exudation control; 2. Large periapical lesions; 3. Dressing; 4. Temporary root filling; 5. Apical inflammatory resorption; 6. Inflammatory resorption following trauma; 7. Apical internal resorption; 8. Internal-external root resorption; 9. Perforations; 10. Transverse root fractures; 11. Incompletely developed pulpless teeth
Heithersay GS. Calcium hydroxide in the treatment of pulpless teeth with associated pathology. J Brit Endo Society 1975;8(2):74-93.
Treatment of Abscessed Teeth
Four months after an auto accident in which the patient’s chin hit the steering wheel, the patient presented with loose and painful lower central incisors. We immediately performed root canals and placed TempCanal in the canals to stimulate healing.
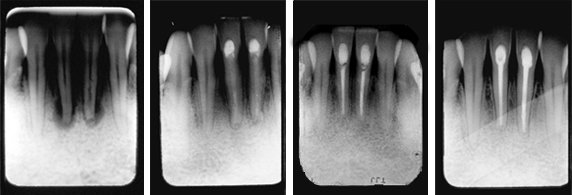
Fig. 1: Radiograph showing abscessed teeth with considerable bone loss.
Fig. 2: Six months after root canals and treatment with TempCanal, radiograph shows bone filling in and healing occurring.
Fig. 3: One year follow up shows healing and obturation with Pulpdent Root Canal Sealer.
Fig. 4: Radiograph taken nine years after final filling shows long term success.
Treatment of Periapical Lesion and Internal Resorption
The patient presented with considerable discomfort and extreme sensitivity to hot, cold and percussion.
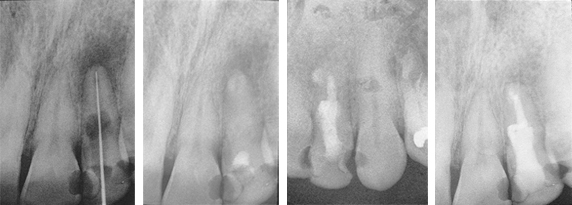
Fig. 1: Diagnostic radiograph shows internal resorption and periapical lesion of the maxillary left lateral. TempCanal was placed at this visit (not shown).
Fig. 2: Radiograph taken 3 months later shows TempCanal in place and periapical healing occurring.
Fig. 3: Radiograph taken after 13 months shows the root canal obturated with Pulpdent Root Canal Sealer using the Pulpdent Pressure Syringe. Note the slight extrusion of sealer beyond the apex and the internal resorption space obturated with sealer.
Fig. 4: Radiograph taken after 19 months shows internal resorption controlled and periapical lesion healed. Note lamina dura. Also shows a portion of the root canal sealer removed and the entire tooth reinforced with Pulpdent HardCord dual cure composite restorative using DenTASTIC as the bonding adhesive.
Treatment of Persistent Periapical Lesion
The Patient had been under treatment for 4 years for a persistent periapical lesion with constant drainage of his left central incisor. Retrograde surgery for removal of the cyst was scheduled. As a temporary measure before surgery, the pulp was removed and TempCanal was placed in the canal. The maxillary left lateral also tested non-vital and was endodontically treated and obturated with Pulpdent Root Canal Sealer at the same visit.
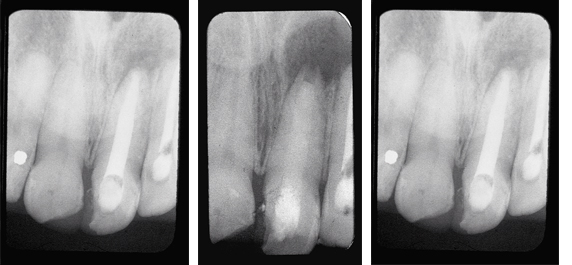
Fig. 1: Radiograph shows periapical lesion involving the maxillary left central and lateral incisors.
Fig. 2: Six weeks following the placement of TempCanal, radiograph shows trabeculation occurring in the periapical area. The surgical procedure was postponed, the TempCanal dressing was changed, and the case was followed until healing of the periapical lesion occurred.
Fig. 3: One year follow up shows healing without surgery and final obturation with Pulpdent Root Canal Sealer using the Pressure Syringe technique.
Hard Tissue Formation
This patient lost his maxillary left central incisor due to a traumatic injury.
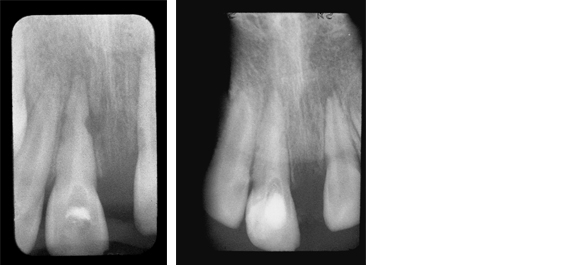
Fig. 1: Radiograph shows external root resorption on the mesial aspect of the maxillary right central incisor. The root canal was filled with TempCanal to promote healing.
Fig. 2: Radiograph taken 3 months later shows remineralization of the mesial aspect of the tooth.
Treatment of Avulsed Tooth
This child presented with avulsed left central and traumatized right central incisors. Two weeks after replantation and splinting, the pulps were removed and Pulpdent Paste was placed in the root canals. The case was followed regularly for 12 months, and the Pulpdent Paste was changed at each visit. After one year, the root canals were obturated with Pulpdent Root Canal Sealer using the Pressure Syringe technique.
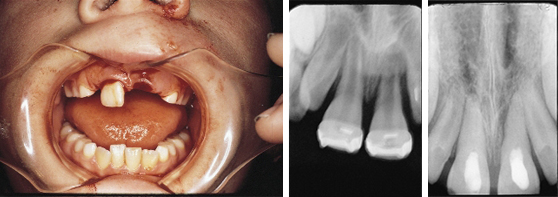
Fig. 1: Photo shows child with avulsed left central and traumatized right central incisor.
Fig. 2: Radiograph taken two weeks following replantation shows replanted tooth, open apices and bone loss. At this visit the root canals were negotiated and Pulpdent Paste was placed as a dressing to stimulate healing and discourage traumatic rejection (not shown).
Fig. 3: Radiograph taken one year after treatment shows Pulpdent Paste in the root canals, apexification and bone fill.
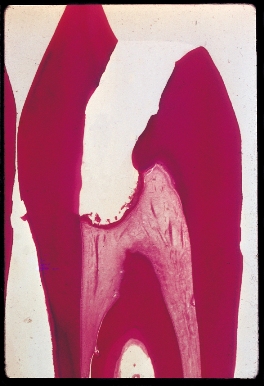
Dentin Bridge Formation
Case 1
This histological section stained with H & E shows new dentin bridge formation two months following pulpal curettage and treatment with Pulpdent Paste.
Case 2
The patient presented in pain with fractured upper central incisors and exposed pulps. Pulpotomies were performed using Pulpdent Paste as the pulpal dressing, which was sealed in place with zinc phosphate cement. Composite restorations were placed using pins for retention. One year after the pulpotomies, the patient returned for more esthetic composite restorations.
A radiograph taken after one-year shows two new dense dentin bridges with composites held in place with pins.
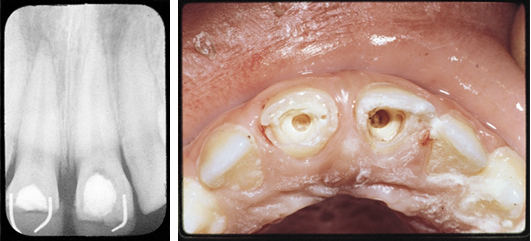
Fig. 1; This is a rare photograph of the new dentin bridges after removal of the composite, pins and zinc phosphate cement.
Fig. 2: Multi-Cal can also be used for dentin bridge formation in direct pulp capping, pulpal curettage and vital calcium hydroxide pulpotomy procedures.
Science & Literature
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between Pulpdent Paste, TempCanal and Multi-Cal?
A: Pulpdent Paste, TempCanal and Multi-Cal are almost identical, can be used interchangeably, and all produce the same results for root canal therapy and vital pulp therapy. They are all non-setting, radiopaque pastes, with pH>12, that contain approximately 40% calcium hydroxide in an aqueous cellulose paste. The differences are in the viscosity and the packaging.
Q: How is Forendo Paste different?
A: Forendo Paste is calcium hydroxide with iodoform in a silicone oil base. It is used only for root canal therapy, not vital therapy, and has all the same indications for root canal therapy as Pulpdent Paste, TempCanal and Multi-Cal.
Q: How long do I leave the root canal treatment paste in the canal?
A: For routine cases, place the paste as a dressing between office visits. For complicated cases involving abscesses and lesions, treatment for one to three months is indicated (change the dressing from time to time). For apexification, hard tissue formation and for traumatic injuries, treatment can be for six to twelve months or even longer.
Q: How do I remove the paste from the canal?
A: These pastes are non-setting. They are easily removed with file and irrigation.
Q: Are these pastes Radiopaque?
A: Yes, all are Radiopaque.
Q: How do I prevent the material from drying out in the syringe?
A: Place a drop of water in the cap, and recap Pulpdent Paste, TempCanal and Multi-Cal immediately after use. Recap Forendo Paste after use, but do not place water in the cap.
Q: What are the differences in viscosity and packaging mentioned above?
A: Pulpdent Paste, the original calcium hydroxide aqueous-methylcellulose pulpal dressing, is a thick paste. It is packaged in a standard 3 mL push syringe and is available in the syringe alone or in a kit with 18-gauge x 1” dispenser needles. TempCanal is a lower viscosity paste packaged in a 3 mL screw syringe. It is available in the syringe alone or in a kit with 22-gauge and 25-gauge x 1.25” dispenser needles. Multi-Cal is a creamy consistency paste, similar in viscosity to TempCanal, and it is available in a standard 3 mL push syringe or in a kit with 4 x 1.2 mL syringes + 22-gauge x ½” applicator tips. Forendo Paste is a creamy paste packaged in a 2.2 gm push syringe with 22-gauge x ½” applicator tips.